

Advanced technologies bring about a change in the educational landscape today. Virtual reality is finding its way into practice in many classrooms, and some of the new exciting ways in which experiments are being carried out involve using this technology. This opens up possibilities for students examining scenarios that might otherwise have been impossible or at best impractical to conduct in a traditional classroom setup.
The objective of the article is to discuss striking a balance between physical and virtual experiments in STEM education. We shall cover why experiments are of high importance, advantages of VR experiments, and how to strike the right balance between these two methods for better learning outcomes. By the end, you will be clearer about how you can effectively integrate VR into your STEM curriculum without giving up the benefits of hands-on experiments.

Experiments are very important in STEM education. They provide a hands-on feel for abstract ideas, thereby making learning enjoyable and memorable. Students learn to visualize theory put into practice with practical lessons, enhancing understanding and retention capabilities.
Experimental learning allows students to really improve their skills in critical thinking and the solving of problems. A student will learn how to formulate hypotheses, observe the outcome, and draw conclusions by following empirical proof through experimentation. It is a hands-on method that is quite useful in helping students comprehend some of the complex principles of science.
These science experiment lesson plans have been essential in STEM education for decades. They not only make learning interactive but also foster a deeper connection with the subject matter. By engaging in these practical lessons, students develop a sense of curiosity and a desire to explore further, laying a strong foundation for future scientific inquiry.
Incorporating both hands-on experiments and virtual experiments can create a more comprehensive and enriching learning experience. While traditional methods provide the tactile and visual cues necessary for understanding, VR education software can offer experiences that are otherwise impossible in a typical classroom setting.
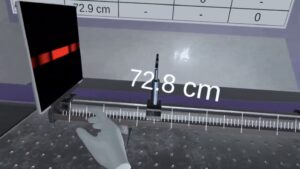
These VR education apps bring with them a wealth of opportunities that traditional experiments simply cannot compare with. First, among these, comes the opportunity to try out experiments that are ethically or legally banned in real life. In a typical school setting, it is not possible to centrifuge human blood and separate it into its constituents because it is considered unethical, and there are legal provisions against such actions. Similarly, it is not possible to safely and ethically replicate the effect of splinters in the skin with real students. VR education software enables these kinds of experiments to be run through—a virtual environment, giving the students all knowledge of the processes involved without any risk.
Besides ethically forbidden experiments, VR technology enables students to conduct those experiments which are impossible in real life. For example, inside the living cells in the virtual laboratory, one is able to change objects and reactions at the micro-level, which in traditional science lesson plans is a purely theoretical part. They could see inside the organs, and see how the tissues interact to perform their functions in a way that diagrams or textbooks are never able to do justice.
Moreover, VR allows students to fiddle around with molecules, atoms, and even the most basic subatomic particles. They can see how these particles interact and emerge to become what comprises the very basis of matter itself, therefore providing a clearer feel—more intuitive—to the very fundamental science being taught. This type of learning experience is almost pricelessly invaluable in creating interest and understanding in STEM education.
Integration of VR education services into the curriculum will, therefore, better place schools at diversifying learning experiences for students to make science more accessible and interactive. The combination of physical and virtual experiments may increase comprehension and student retention, making them well-prepared for further developments in science.
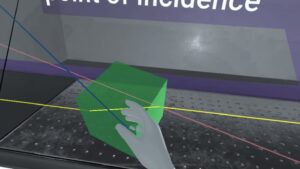
Although impressive, these very benefits of VR education cannot substitute traditional hands-on experiments in the laboratory. Thus, physical experiments provide a sense of tacility core to developing real-life skills. For instance, measuring liquids, manipulating laboratory equipment, and observing chemical reactions enhance understanding of scientific tenets through ‘touch-and-feel’ interaction.
Experiments of a classic nature, for example, growing plants in different conditions to explain photosynthesis or measurement of electrical circuits to understand the basics of the flow of electric current, are absolutely impossible to replace. Those activities not only fix theoretical knowledge but also develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. They teach proper safety measures that one is supposed to observe, working techniques to be implemented in a laboratory, and thus prepare students for further work in the science lab.
On the other hand, VR education services are perfect for experiments that are impractical or impossible to conduct in a real school setting. Virtual experiments can simulate scenarios that are too dangerous, expensive, or complex to recreate physically. For example, students can use VR education apps to explore molecular structures, dive into the human bloodstream, or conduct high-energy physics experiments—all from the safety of their classroom.
VR education software complements traditional methods by offering interactive and immersive experiences that enhance the understanding of complex subjects. For instance, students can virtually dissect an animal without ethical concerns, or manipulate atoms and molecules to see chemical reactions at the atomic level. This can make abstract concepts much more tangible and comprehensible.
Position Statement
We do: Using VR in education has huge potential, but shall not replace the actual experiments; it will supplement them. For this reason, we will prefer a balanced approach where VR technology shall be used to enhance learning and not for its own sake as some fancied technology. Integrate both physical and virtual experiments, and one gets a richer, more versatile educational experience that caters to a variety of learning styles and needs.
Get Started with VR Experiments
Want to see for yourself what’s possible in VR education? Fill out this form on our request demo page to get free access to a VR simulation containing a virtual experiment. Don’t have a VR? No problem. There are ways to experience the content anyway. We offer solutions to make sure you’re still able to discover and learn from our simulations.
In other words, experiments are essential parts of STEM education to make it practical, hands-on, and to come up with a deep understanding and retention. Where traditional hands-on experiments play an invaluable role in foundational learning, VR education apps and VR education software are opening new avenues for conducting complex and otherwise impractical experiments.
It is all about balance—physical and virtual experiments, while not necessarily being mutually exclusive, should be duly balanced. It is possible to include VR in the syllabus to make the learning experience at school more interactive and holistic in nature. At the same time, it should be adopted in a discreet manner to supplement and complement the present system of learning, not to replace it altogether.
Looking ahead, STEM education will be balanced by the approach that marries the best of both worlds. Further innovating and integrating new technologies will go on to provide students with increased richness and versatility of learning experience for sustainability of challenges and opportunities reaching forward from the future.
Frequently Asked
XReady Lab offers the largest K–12 STEM VR and Web/PC library with an AI Tutor. The packages include biology, physics, chemistry, and math, covering topics from primary school through high school.
All content is designed to align with major curricula and deliver engaging, interactive learning experiences. New simulations are added monthly.
XReady Lab’s simulations are aligned with IB, Cambridge IGCSE, AS & A Levels, NGSS, College Board, Common Core, TEKS, CBSE, BNCC, the National Curriculum for England, the Italian secondary school curriculum (Scuola Secondaria), and the National Curriculum of the Netherlands (VMBO, HAVO, VWO).
Career Packs are VR simulation bundles that let students explore STEM careers in practice. Current packs include: Future Doctor, Future Nurse, Future Engineer, Future HVAC Engineer, Future Biotechnologist, Future Astronomer, Future Neuroscientist.
New Career Packs are added regularly.
XReady Lab Superhuman AI Tutor works like a real tutor, guiding students step by step instead of giving ready-made answers. It focuses on reasoning, problem-solving, and explaining mistakes to build real understanding.
Created by international STEM Olympiad winners and coaches, it helps prepare for exams, increases memory retention by 40%, and works in real time in both VR and desktop formats with an internet connection.
XReady Lab packages include complimentary teacher training and ready-to-use Lesson Plans and Engagement Playbooks to support engaging lessons.
They guide teachers in integrating VR/web/PC simulations with clear objectives, step-by-step instructions, classroom management strategies, reflection activities, assessments, and technical checklists — helping teachers run effective lessons beyond the simulations themselves.
Simply fill out the free demo form here to get access to demo XReady Lab simulations.
We start with consultation: our team helps plan the VR classroom for your school. You need internet access and a suitable room — allocate about 5 x 5 feet (1.5 x 1.5 m) per student. One headset per two students works well.
Devices and licenses: schools can use existing Meta Quest or Pico devices and purchase licenses, or we can offer discounted devices or a turnkey solution with pre-installed content.
After purchase, we guide device setup and content installation and provide teacher training.
Teachers learn how to run VR lessons using Lesson Plans and Engagement Playbooks, manage screen casting and paired learning, and keep students engaged.
Ongoing support is always available.
VR lessons typically last 5–15 minutes, depending on the simulation, with a recommended class size of up to 20 students. Screen casting is supported and compatible with selected teacher management systems, allowing teachers to launch simulations remotely, monitor progress, and view all devices during lessons.
Teachers are supported with Lesson Plans and Engagement Playbooks that include learning objectives, step-by-step lesson flow, classroom scenarios, reflection questions, practical assignments, and assessment guidance.
XReady Lab is available worldwide and supports 75+ languages. Today, it is used by 800+ schools and 150,000+ students across the globe.
XReady Lab simulations are offered through flexible licensing packages, depending on the format and subjects you need:
If you already have VR headsets, you only purchase licenses. If not, we can also help you choose the most cost-effective setup and licensing model for your school or family.
XReady Lab works with the most widely used standalone VR headsets in schools:
All supported devices are standalone (no PC required), making them easy to deploy and manage in a school environment.
Yes. XReady Lab supports open ecosystems, not closed platforms. Schools can freely use third-party VR content alongside XReady Lab on Meta Quest and PICO headsets.
We encourage schools to diversify their VR classrooms with high-quality educational apps and can recommend tested solutions, helping expand learning beyond STEM into subjects like design, history, environmental studies, and soft skills.
XReady Lab follows school VR safety best practices. VR is recommended for students 10–12+, with short 5–15 minute sessions and seated or safe-zone use under teacher supervision, supported by screen casting.
First-time users adapt gradually. Students with medical conditions require parental and school approval, and hygiene is ensured through regular headset cleaning and replaceable face covers.
Families can access XReady Lab simulations at home in two ways: